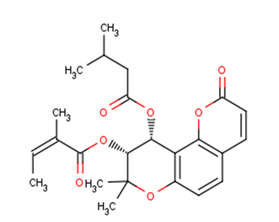
Praeruptorin C
CAS No. 72463-77-5
Praeruptorin C( —— )
Catalog No. M19039 CAS No. 72463-77-5
Praeruptorin C has been widely used as an antioxidant and a calcium antagonist to treat diseases.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 86 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 149 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 257 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 385 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePraeruptorin C
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPraeruptorin C has been widely used as an antioxidant and a calcium antagonist to treat diseases.
-
DescriptionPraeruptorin C has been widely used as an antioxidant and a calcium antagonist to treat diseases. Praeruptorin C partially protects cortical neurons by inhibiting the expression of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors and regulating the Bcl-2 family. Praeruptorin C can reduce vascular hypertrophy in isolated rat hypertrophied smooth muscle cells, and this is associated with improvement of smooth muscle cells [Ca2+]i level, nitric oxide content and cellular signal transdution of protein kinase C and Gi.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorAntioxidant
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number72463-77-5
-
Formula Weight428.48
-
Molecular FormulaC24H28O7
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 25 mg/mL (58.35 mM)
-
SMILESCC=C(C)C(=O)OC1C(C2=C(C=CC3=C2OC(=O)C=C3)OC1(C)C)OC(=O)CC(C)C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Picfeltarraenin IV
Picfeltarraenin IV is a natural product from Picria felterrae Lour.
-
L,L-Dityrosine hydro...
L,L-Dityrosine is a constituent of acid hydrolysates of a number of biological materials, including the insect cuticular resilin.?
-
BPH-715
BPH-715 inhibits the liver-stage growth of P. falciparum with an IC50 of 10 μM for P. falciparum exoerythrocytic forms in HepG2 cells.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


